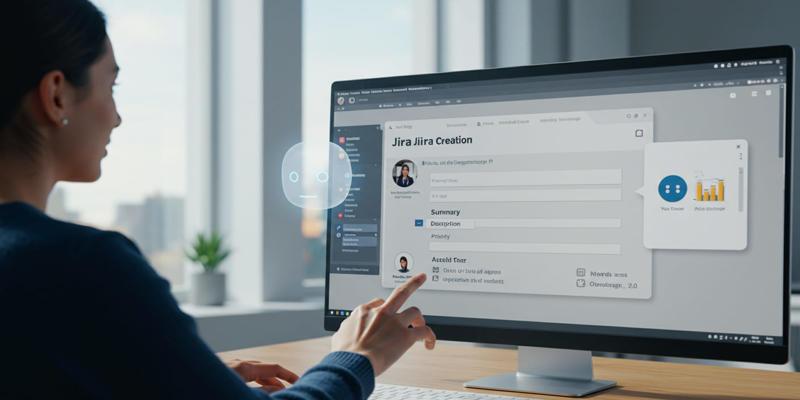
 The world of software development and project management is very fast, and the importance of efficiency and accuracy cannot be underestimated. One of the most popular project management and issue-tracking applications, Jira provides a clear way of work organization and task tracking within a team. Manual ticket creation can take up a good deal of time and give room to human error. Automation of this process also saves time, cuts down on errors, and increases productivity. We will understand how to automate the creation of tickets in Jira with the help of the OpenAI Agents SDK, what the procedure is, what tips we can follow, and under which aspects the system can be improved to expand its automation.
The world of software development and project management is very fast, and the importance of efficiency and accuracy cannot be underestimated. One of the most popular project management and issue-tracking applications, Jira provides a clear way of work organization and task tracking within a team. Manual ticket creation can take up a good deal of time and give room to human error. Automation of this process also saves time, cuts down on errors, and increases productivity. We will understand how to automate the creation of tickets in Jira with the help of the OpenAI Agents SDK, what the procedure is, what tips we can follow, and under which aspects the system can be improved to expand its automation.
The OpenAI Agents SDK is a development kit that can be used to create smart virtual agents that understand user intent and take complex actions. Such agents are able to understand the natural language request issued by the users and, through he implementation of an API, perform targeted actions.
Regarding Jira, the SDK will be able to code agents that will read what the user writes about an issue or a task and then translates it into a ticket in structured Jira that is sing AI-powered cognition with Jira API, these agents eliminate manual and repetitive tasks and facilitate the disappearance of the bottleneck of manually entered data, as well as guarantee to create tickets more quickly and in a specific format.
The first action is to prepare the environment in which you will configure and deploy your ticket automation agent. Start by ensuring you possess administrative or proper API access to a Jira system to which it is possible to create programmatically formed tickets.
At the same time, make sure that you have an account with OpenAI with permissions to the Agents SDK. The SDK can interface with more common programming languages, including Python and JavaScript, and you will want to install the required packages for the project.
Using Jira in a programmatic manner requires sound authentication. The API tokens or OAuth mechanisms are mainly used. You will have to produce an API token in your Jira profile and attribute it safely in your agent configuration options.
Effective authentication enables your AI agent to make authorized API calls to create tickets and perform other management operations, and guards against unauthorized use. The best practice is to manage authentication parameters using environment variables or secret managers in order to avoid the problem of exposure.
Before any automation is introduced, one should have an idea of how the AI agent will work and what relationships it might establish with users. In this case, the major task of the agent is to process user inputs that consist of the description of the issue or ask, and then extract the describing ticket information and generate Jira tickets, based on it.
Customers may submit a request in a variety of ways, e.g,,. as follows: There is a problem when logging in with the user account.t There is an issue with the latency in the payment system. Please respond. There is a high-priority issue with the latency in the payment system.
A key element of this automation is in decoding free-form user queries to provide the structured ticket information. Using the language models that OpenAI has developed and integrating them into the SDK is very useful in serving this task.
The tool can be triggered to understand some of the important aspects, such as issue summary details, detailed descriptions, priority levels, affected components, and assignments, using the input in the form of natural language. It is supple enough to allow discussing variations and incomplete data.
A good way to do this is to create prompts that will help the AI to divide text input and create short, clear attributes of the Jira ticket. Facilitated by the context knowledge, such an NLP element contributes to the pleasant user experience, which is not enforced under a strict form or a somewhat strict type of keyboard input.
Once the ticket information has been scraped, the AI agent now has to assemble the information to conform to the format that Jira requires. The agent is built to create an appropriately constructed request and then submit it to the Jira ticket creation API.
Error handling also covers probing the Jira API, looking for either success, affirmation, or failure. In case of a dispute or information omission, the agent is able to clarify or rectify the user- another way of ensuring the automation process is robust and reliable.
Clearness in communicating to users induces trust in automated systems. Upon successful creation of the ticket, the agent reports back to the user with the ticket ID or key with a direct link to view the new ticket in Jira.
This feedback will help such users learn that their problems have been registered and await resolution by the concerned departments. When the process of creating a ticket cannot succeed, the agent is polite and clearly explains why it is not going through and how the process can be recharged, thus ensuring there is a minimum of frustration.
As core automation around creating tickets is established, consider how to layer more sophistication and value on top of the agent. The prospects of enhancement are as follows:
Not only do such developments enhance the smartness and utility of the agent, but they also enhance the agility and responsiveness of your project management processes.
Automatically creating a Jira ticket using the OpenAI Agents SDK has the following definite advantages:
By automating the process of creating tickets in Jira using the OpenAI Agents SDK, organizations will automate how they associate their details and manage their system. This tutorial has explained the major steps- environment preparation and authentication, integration of natural language processing, and creation of smooth user responses.
With the advance of AI technology and teams becoming accustomed to the idea of automation, integration of tools such as OpenAI Agents SDK will be a key to remaining competitive and responsive in a fast-paced business environment.

Model behavior mirrors human shortcuts and limits. Structure reveals shared constraints.

Algorithms are interchangeable, but dirty data erodes results and trust quickly. It shows why integrity and provenance matter more than volume for reliability.

A technical examination of neural text processing, focusing on information density, context window management, and the friction of human-in-the-loop logic.

AI tools improve organization by automating scheduling, optimizing digital file management, and enhancing productivity through intelligent information retrieval and categorization

How AI enables faster drug discovery by harnessing crowdsourced research to improve pharmaceutical development

Meta’s AI copyright case raises critical questions about generative music, training data, and legal boundaries

What the Meta AI button in WhatsApp does, how it works, and practical ways to remove Meta AI or reduce its presence

How digital tools like Aeneas revolutionize historical research, enabling faster discoveries and deeper insights into the past.

Maximize your AI's potential by harnessing collective intelligence through knowledge capture, driving innovation and business growth.

Learn the LEGB rule in Python to master variable scope, write efficient code, and enhance debugging skills for better programming.

Find out how AI-driven interaction design improves tone, trust, and emotional flow in everyday technology.

Explore the intricate technology behind modern digital experiences and discover how computation shapes the way we connect and innovate.